Survey uncovers critical OT security challenges

Fortinet®, a global provider of comprehensive, integrated, and automated cybersecurity solutions, has released its Global State of Operational Technology and Cybersecurity Report for 2022.
While industrial control environments remain a target for cybercriminals, with 93% of Operational Technology (OT) organizations reporting an intrusion in the previous 12 months, the report uncovered widespread gaps in industrial security and identified opportunities for improvement.
“This year’s global State of OT and Cybersecurity Report demonstrates that while OT security has the attention of organizational leaders, critical security gaps remain. PLCs designed without security, continued intrusions, a lack of centralized visibility across OT activities, and growing connectivity to OT are some of the critical challenges these organizations need to address. Security converged into the OT networking infrastructure, including switches and access points and firewalls, is essential to segment the environment. This combined with a platform that spans OT, converged OT/IT and IT provides end-to-end visibility and control,” said John Maddison, EVP of Products and CMO at Fortinet.
Key findings of the report include:
- OT activities lack centralized visibility, increasing security risks. According to the Fortinet report, only 13% of respondents have achieved centralized visibility of all OT activities. Furthermore, only 52% of organizations can track all OT activities from the security operations center (SOC). Simultaneously, 97 percent of global organizations regard OT as a moderate or significant factor in overall security risk. According to the report’s findings, a lack of centralized visibility contributes to organizations’ OT security risks and weakened security posture.
- OT security intrusions significantly impact organizations’ productivity and their bottom line. The Fortinet report found that 93% of OT organizations experienced at least one intrusion in the previous 12 months, with 78 percent experiencing more than three intrusions. As a result of these intrusions, nearly half of organizations experienced an operational outage, affecting productivity, with 90 percent of intrusions requiring hours or longer to restore service. Furthermore, one-third of respondents reported that security intrusions had an impact on revenue, data loss, compliance, and brand value.
- Ownership of OT security is not consistent across organizations. According to the Fortinet report, OT security management is primarily associated with director or manager roles ranging from Director of Plant Operations to Manager of Manufacturing Operations. Only 15% of survey respondents say that the CISO is in charge of OT security in their organization.
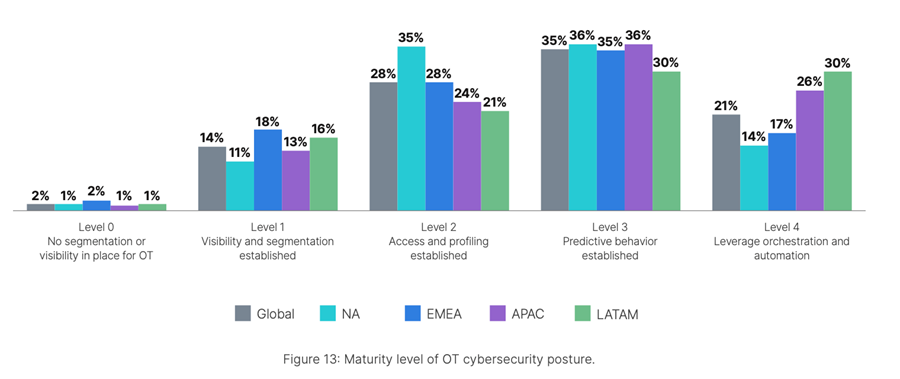
- OT security is gradually improving, but security gaps still exist in many organizations. Only 21% of organizations have reached level 4, which includes orchestration and management, when asked about the maturity of their organization’s OT security posture. Notably, a higher proportion of respondents in Latin America and APAC have reached level 4 than in other regions. More than 70% of organizations are in the middle stages of developing a mature OT security posture. Simultaneously, organizations face challenges when employing multiple OT security tools, further compromising their security posture. According to the report, the vast majority of organizations use two to eight different vendors for their industrial devices and have between 100 and 10,000 devices in operation, which adds complexity.
Best Practices to Overcome OT Security Challenges
Fortinet’s global 2022 State of Operational Technology and Cybersecurity Report identified ways for organizations to address OT system vulnerabilities and strengthen their overall security posture. Organizations can address their OT security issues by:
- Establish Zero Trust Access to prevent breaches. As more industrial systems are connected to the network, Zero Trust Access solutions ensure that any user, device, or application that lacks the necessary credentials and permissions is denied access to critical assets. Zero Trust Access solutions can help to advance OT security efforts by defending against both internal and external threats.
- Implementing solutions that provide centralized visibility of OT activities. Centralized, end-to-end visibility of all OT activities is key to ensuring organizations strengthen their security posture. According to Fortinet’s report, top-tier organizations – which make up the 6% of respondents who reported no intrusions in the past year – were more than three times as likely to have achieved centralized visibility than their counterparts who suffered intrusions.
- Consolidating security tools and vendors to integrate across environments. To remove complexity and help achieve centralized visibility of all devices, organizations should look to integrate their OT and IT technology across a smaller number of vendors. By implementing integrated security solutions, organizations can reduce their attack surface and improve their security posture.
- Deploying network access control (NAC) technology. Organizations that avoided intrusions in the past year were more likely to have role-based NAC in place, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access specific systems critical for securing digital assets.